Chapter 3
 3.2 Discovering phonemes
3.2 Discovering phonemes
I.Brainstorming
How to discover phonemes?
II. Contrastive distribution – phonemes
1. Definition of contrastive distribution
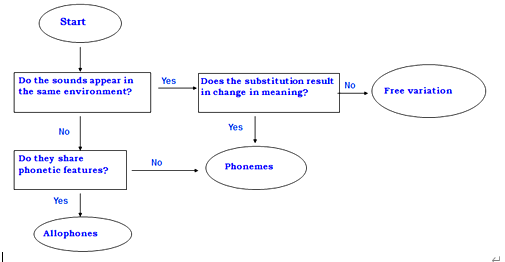
If sounds appear in the same environment, they are said to be in contrastive distribution.Typical contrastive distribution of sounds is found in minimal pairs and minimal sets.
The overwhelming majority of the consonants and vowels represented by the English phonetic alphabet are in contrastive distribution.
Some sounds can hardly be found in contrastive distribution in English. However, these sounds are distinctive in terms of phonetic features. Therefore, they are separate phonemes.
2. Minimal pair & Minimal sets
A minimal pair consists of two words that differ by only one sound in the same position. For example, “pin” and “bin”, “pin” and “pen”, “pin” and “ping” are each a minimal pair.
Minimal sets are more than two words that are distinguished by one segment in the same position.
III. Complementary distribution – allophones
• Sounds that are not found in the same position are said to be in complementary distribution.
• If segments are in complementary distribution and share a number of features, they are allophones of the same phoneme.
IV. Free variation
• If segments appear in the same position but the mutual substitution does not result in change of meaning, they are said to be in free variation. Segments in free variation are generally dialectal variation.
V. The discovery procedure
VI. Conclusion
The distribution of sounds falls into three types, each of which is the basis for judging whether the sounds distinguish meaning.
