Answer

I.
1. 300 2. eight 3. 450-1150 4. 1150-1500 5. two
6.
full of endings 7. analytic 8. Italian 9. small 10. little
II.
1.T 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. F 6. F 7. T 8. T 9. F 10. T
III.
1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. C 6. D 7. A 8. A
IV.

V.
1.
He fastened the lid to the box with a nail.
2.
Their visit took us by surprise.
3.
Mrs. Smith is an English coach.
4.
The food at the restaurant filled me with disgust.
5.
William will be the referee of the football match.
6.
He became a cripple in an accident.
VI.
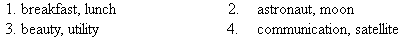
VII.
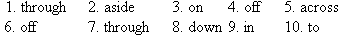
VIII.
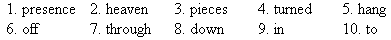
IX.
This sentence has a very vague idea because a number of superordinates
are used such as a magnificent building, destroyed, some time ago,
in a large city in England. The sentence can be improved like this:
"The Royal Hotel in London was burnt down last Wednesday night.'
In the improved sentence, the subordinates the Royal Hotel, in London,
burnt down, last Wednesday night are used respectively instead of
a magnificent building, in a large city, destroyed, some time ago,
the meaning of the sentence becomes clear and definite. Therefore, it
is much better.
X.
1. Vocabulary can be classified by different criteria into different
types. By use frequency, words fall into the basic word stock and non-basic
vocabulary. Basic vocabulary is small in number but forms the core of
the language and enjoys high frequency of use. Non-basic vocabulary
contains such words as terminology, jargon, slang, argot, archaism,
neologism, which have a relatively limited use. By notion, words can
be divided into content words and functional words. Content words have
clear notions such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs; functional
words cover prepositions, pronouns, articles, conjunctions, etc., whose
major functions are to help make sentences. By origin, words can grouped
into native words and foreign words. Native words refer to the words
of Anglo-Saxon origin, which are small in number but form the mainstream
of the basic word stock. Foreign words are borrowed from other languages
and make up 80% of the whole English vocabulary. There are other ways
too, for example, by morphological structure, formality, emotionality,
and so on.
2. A general-purpose dictionary usually provides commonly used words
in alphabetical order, spelling, pronunciation, meaning, grammar information,
usage, and supplementary matter in different scope.
Entry
words. The selection of words depend on the dictionary, the bigger
the dictionary, the larger the number of less common words are contained.
Spelling.
The dictionary provides standard spelling forms together with usually
the British or American variants,
Pronunciation.
It provides the widely accepted pronunciation with usually British and
American variants.
Meaning.
It provides the most common meanings. Ways of definition vary, some
in sentence forms, the most in standard phrases. The number of meanings
is listed according to the size of the dictionary, the bigger, the more.
Grammar
information. It usually includes such information as part of speech,
countability of nouns, forms of irregular verbs and adjective, verb
patterns, register, and so on.
Usage. A good general-purpose dictionary provides a lot of examples
to illustrate usage, particularly around verbs. Some even include language
notes and discriminate synonyms and near-synonyms.
Supplementary
matter. The amount of the supplementary matter varies in dictionaries.
Usually, we can find tables of numbers, weights and measures, pronunciation
guide, irregular verbs, etc.
|

