当前位置:课程学习>>第十章 多线程>>文本学习>>知识点二
知识点二 线程控制

一、线程的生命周期
线程的4种状态包括:创建、运行、阻塞和死亡。线程的状态转换如图10.1所示。当使用new创建线程对象时,线程对象产生,此时处于创建态。当调用该对象的start方法时,线程进入运行态,开始执行run方法中所包含的代码。如果当前线程进行I/O操作、执行sleep、wait、join操作或试图进行synchronized操作获取同步锁而不成功时,进入阻塞状态,需要CPU进行线程的调度和切换。当所需要的条件满足时,线程从阻塞状态回到运行态。当run方法执行完毕后,线程进入死亡态。进入死亡态的线程,等待系统撤销并释放所占用的资源。如果想重新运行线程,只有重新使用new创建对象并调用start方法。
其中,run方法是通过调用start方法来间接调用的,只有调用start方法时,系统才会为线程对象分配运行所需要的资源,并在分配好资源后调用run方法。如果在程序中直接调用run方法,则run仅作为一个普通的方法,不会以线程的方式并发运行。
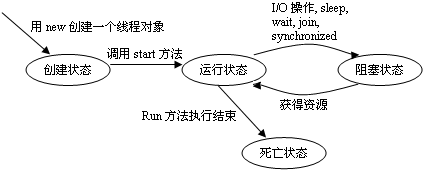
图 10.1 线程生命周期
二、线程的控制
1. 启动线程
通过调用线程对象的start方法来启动线程,该方法会自动调用run方法。如果直接调用run方法的话,就不会启动线程,而是调用了一个普通方法而已。
2. 终止线程
终止线程的方法,是使run方法执行结束。在设计run方法的时候,尽可能随时检测代码段是否终止,以及时退出。
volatile boolean stopFlag = false;
public void run()
{
while (true)
{
if (stopFlag)
return;
// do other things.
}
}
将线程的stopFlag置为true,可以正常终止线程。
3. 休眠线程
sleep方法使线程处于休眠状态,方法的使用情况为:
public void sleep(long millis)
其中,millis指定线程休眠的毫秒,给其他线程运行的机会。时间到达后线程被唤醒,且收到InterruptedException异常。
sleep方法必须放在try catch中,如:
try {
myThread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
当一个线程休眠的时间到达或者被调用interrupt方法,线程即被唤醒,返回运行状态,从而继续运行。
4. 中断线程
当调用线程对象的interrupt方法,无论线程处于运行状态还是阻塞状态,都首先将线程对象的“线程中断”标记设为true,如果线程对象处于可中断或者可唤醒的阻塞状态(由sleep, wait, join等方法引起的),如果是则唤醒线程,从阻塞状态返回运行状态,同时线程对象还接受到InterruptedException异常。
如果线程对象处于创建状态或死亡状态,调用interrupt方法会产生IllegalThreadStateException异常。
调用线程的isInterrupted方法检测线程是否被中断过,即返回“线程中断”标记的值(true或false,true表示被中断过)。
5. 检测线程状态
public final Boolean isAlive()
该方法用于测试一个线程是否是活动的,若一个线程调用了start方法,且不处于死亡状态,则认为该线程是活动的,返回true,否则返回false。
没有方法能够测试一个线程处于运行状态或是阻塞状态。
6. 线程优先级和线程调度
线程的优先级表示该线程的紧急程度,线程越紧急,被处理器调度执行的机会就越大。在Thread类中优先级取值范围为1到10,并定义了3个表示线程优先级的常量:
public static final int MAX_PRIORITY = 10; // 最高优先级
public static final int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; // 默认优先级
public static final int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; // 最低优先级
数值越大,优先级越高。getPriority和setPriority用于获取和设置线程的优先级。方法的定义分别为:
public int getPriority()
public void setPriority(int newPriority)
7. 线程协作
当线程执行到某一阶段时,要等待其他线程之行完毕后才能继续执行。这个线程间协作的功能可以通过join方法来实现,其格式为:
public final void join()
该方法使线程对象进入阻塞状态,直到被调用join方法的线程进入死亡状态后才返回运行状态继续执行。
public final void join(long millis)
该方法使线程对象进入阻塞状态,直到被调用join方法的线程进入死亡状态或者指定的millis毫秒时间到才返回运行状态继续执行。
join方法应该放在try catch块中,如:
Thread myThread = new Thread();
myThread.start();
try {
myThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
【例10.4】将10.1中的弹跳小球实例改写为线程程序,用以实现控制的功能。
//BouncerThread.java
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class BouncerThread extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
JPanel canvas = new JPanel();
JPanel btnPanel = new JPanel();
JButton startBtn = new JButton("start");
JButton stopBtn = new JButton("stop");
BallThread ball;
public BouncerThread() {
getContentPane().add(canvas);
getContentPane().add(canvas, BorderLayout.CENTER);
getContentPane().add(btnPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
btnPanel.add(startBtn);
btnPanel.add(stopBtn);
startBtn.addActionListener(this);
stopBtn.addActionListener(this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BouncerThread bouncer = new BouncerThread();
bouncer.setTitle("Bouncer");
bouncer.setSize(300, 200);
bouncer.setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource() == startBtn) {
ball = new BallThread(canvas);
ball.start();
}
if (e.getSource() == stopBtn)
ball.stopBouncer();
}
}
class BallThread extends Thread {
private JPanel canvas;
private int radio;
private int x_pos, y_pos;
private int x_dis, y_dis;
private int c_width, c_height;
volatile boolean stopFlag = false;
public BallThread(JPanel c) {
canvas = c;
c_width = canvas.getWidth();
c_height = canvas.getHeight();
radio = 6;
// 小球起始位置取随机值
x_pos = (int) (Math.random() * c_width);
y_pos = (int) (Math.random() * c_height);
// 每次移动距离为半径/2
x_dis = y_dis = radio / 2;
}
public void run() {
draw();
while (true) {
if (stopFlag)
return;
move();
try {
sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public void draw() {
Graphics g = canvas.getGraphics();
g.fillOval(x_pos, y_pos, radio, radio);
g.dispose();
}
public void move() {
Graphics g = canvas.getGraphics();
g.setXORMode(canvas.getBackground());
g.fillOval(x_pos, y_pos, radio, radio);
x_pos += x_dis;
y_pos += y_dis;
if ((x_pos <= 0) || (x_pos >= c_width - x_dis))
x_dis *= -1;
if ((y_pos <= 0) || (y_pos >= c_height - y_dis))
y_dis *= -1;
g.fillOval(x_pos, y_pos, radio, radio);
g.dispose();
}
public void stopBouncer() {
stopFlag = true;
// 清除小球痕迹
Graphics g = canvas.getGraphics();
g.setXORMode(canvas.getBackground());
g.fillOval(x_pos, y_pos, radio, radio);
}
}
上面的程序实现了对小球弹跳过程的控制,stop按钮的点击事件可以得到响应。
