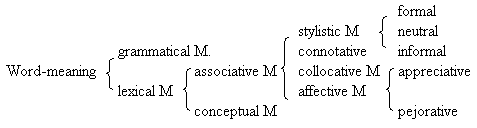
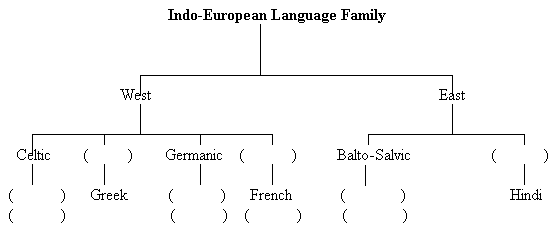
| Answer
I. 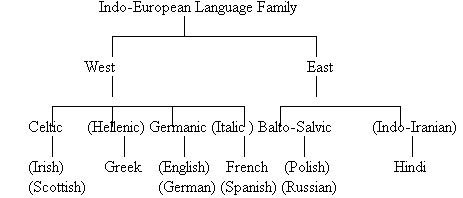 II.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. F 6. T 7. F 8. T 9. F 10. T III.
1. D 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. D 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. D 10. D VI.
1. minimal, meaning, syntactic 2.
sound, meaning 3.
core 4.
Anglo-Saxon VII.
1. 首字母拼音法 |